# Physical material to Simplygon material
The Physical Material is the new standard material in Max 2021 and later, and although we have a basic implementation for mapping most properties there might be a need for customizing material channels. This section goes through how to map Physical material properties to Simplygon and back through scripting and shading networks. It is recommended to read Shading network concepts and Simplygon Shading Network functions before proceeding.
# Scripting
To translate a Physical material to a Simplygon material you would most likely want to extract certain properties from your material. To map a specific material property to Simplygon we need to identify the name of the Physical Material we want to override, as well as the material properties we are interested in, here's a list of "Physical Material" properties that we've gathered so far:
| Type | Property name | Texture slot | (Default) Simplygon channel | Mapping through name | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| int | material_mode | Not required (changes the view mode of the material) | |||
| float | base_weight | base_weight | ColorNode | ||
| Point4* | base_color | base_color | ColorNode | ||
| float | reflectivity | reflectivity | ColorNode | ||
| float | roughness | roughness | ColorNode | ||
| bool | roughness_inv | roughness | Used internally when no override Inverts roughness input | ||
| float | metalness | metalness | ColorNode | ||
| Point4* | refl_color | refl_color | ColorNode | ||
| float | diff_roughness | diff_roughness | ColorNode | ||
| bool | brdf_mode | No appropriate mapping | |||
| float | brdf_low | ColorNode | Only through color node | ||
| float | brdf_high | ColorNode | Only through color node | ||
| float | brdf_curve | ColorNode | Only through color node | ||
| float | anisotropy | ColorNode | Only through color node | ||
| float | anisoangle | ColorNode | Only through color node | ||
| int | aniso_mode | No appropriate mapping | |||
| int | aniso_channel | No appropriate mapping | |||
| float | transparency | transparency | ColorNode | ||
| Point4* | trans_color | trans_color | ColorNode | ||
| float | trans_depth | trans_depth | ColorNode | ||
| float | trans_roughness | trans_roughness | ColorNode | ||
| bool | trans_roughness_inv | trans_roughness | Used internally when no override Inverts roughness input | ||
| bool | trans_roughness_lock | trans_roughness | Used internally when no override true -> use roughness map false -> use trans_roughness | ||
| float | trans_ior | trans_ior | stored as value / 50.f (0.0f - 1.0f) | ||
| bool | thin_walled | No appropriate mapping | |||
| float | scattering | scattering | ColorNode | ||
| Point4* | sss_color | sss_color | ColorNode | ||
| float | sss_depth | sss_scale | ColorNode | Stored in sss_scale | |
| float | sss_scale | sss_scale | ColorNode | (sss_depth / 1000.f) * sss_scale | |
| Point4* | sss_scatter_color | sss_scatter_color | ColorNode | No automatic back mapping as there is no texture slot in Physical Material | |
| float | emission | emission | ColorNode | ||
| Point4* | emit_color | emit_color | ColorNode | ||
| float | emit_luminance | emit_luminance | ColorNode | Stored as emit_luminance / 1000.f (0.0f - 1.0f) | |
| float | emit_kelvin | emit_kelvin | ColorNode | Stored as Color::FromKelvinTemperature(fKelvin) / 1.78516805f (0.0f - 1.0f) | |
| float | coating | coating | ColorNode | ||
| Point4* | coat_color | coat_color | ColorNode | ||
| float | coat_roughness | coat_roughness | ColorNode | ||
| bool | coat_roughness_inv | coat_roughness_inv | |||
| float | coat_affect_color | coat_affect_color | ColorNode | ||
| float | coat_affect_roughness | coat_affect_roughness | ColorNode | ||
| float | coat_ior | coat_ior | Stored as coat_ior / 5.f (0.0f - 1.0f) | ||
| Texmap* | base_weight_map | 0 | base_weight | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | base_color_map | 1 | base_color | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | reflectivity_map | 2 | reflectivity | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | refl_color_map | 3 | refl_color | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | roughness_map | 4 | roughness | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | metalness_map | 5 | metalness | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | diff_rough_map | 6 | diff_rough | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | anisotropy_map | 7 | TextureNode | ||
| Texmap* | aniso_angle_map | 8 | TextureNode | ||
| Texmap* | transparency_map | 9 | transparency | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | trans_color_map | 10 | trans_color | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | trans_rough_map | 11 | trans_rough | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | trans_ior_map | 12 | trans_ior | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | scattering_map | 13 | scattering | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | sss_color_map | 14 | sss_color | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | sss_scale_map | 15 | sss_scale | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | emission_map | 16 | emission | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | emit_color_map | 17 | emit_color | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | coat_map | 18 | coat | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | coat_color_map | 19 | coat_color | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | coat_rough_map | 20 | coat_rough | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | bump_map | 30 | bump | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | coat_bump_map | 31 | coat_bump | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | displacement_map | 32 | displacement | TextureNode | |
| Texmap* | cutout_map | 33 | cutout | TextureNode | |
| bool | base_weight_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | base_color_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | reflectivity_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | refl_color_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | roughness_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | metalness_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | diff_rough_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | anisotropy_map_on | ||||
| bool | aniso_angle_map_on | ||||
| bool | transparency_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | trans_color_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | trans_rough_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | trans_ior_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | scattering_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | sss_color_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | sss_scale_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | emission_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | emit_color_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | coat_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | coat_color_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | coat_rough_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | bump_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | coat_bump_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | displacement_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| bool | cutout_map_on | Used internally when no override | |||
| float | bump_map_amt | ColorNode | |||
| float | clearcoat_bump_map_amt | ColorNode | |||
| float | displacement_map_amt | ColorNode |
Now that we have all available material properties, let's head over to the export section and do some prototyping!
# Export
The first thing we need to do to create a shading network is to specify the material name we want to override. The line below tells the Simplygon plug-in that there's a shading network available for the specific material.MaterialName in this case is the name of the Physical Material in the 3ds Max material browser/editor, usually something like '01 - default' for new materials.
Simplygon's texture nodes maps directly to the Physical material's texture property via name, let's use base_color_map (Texmap*) from the table above for this tutorial.
Color nodes work pretty much in the same way, let's use base_color (Point4*). This line is just an illustration, we'll not use it in our shading network.
To connect the shading network to a material channel we will add another line to our script. A material channel can be named anything, but keep in mind that it directly maps to the channel name of the material caster in the settings, if you intend to cast the material channel to a texture that is.
Let's add the bump_map texture to the bump material channel, this should be fairly easy from what we have learned.
Before calling the Simplygon function there are some optional settings that can be set, for example texture output directory which can make life easier when importing / handling textures. Remember to select the asset before running the Simplygon command, otherwise the command will be ignored.
The final export script:
For properties that are not automatically mapped, such as int, bool and float properties, these are accessible through the Physical Material via MaxScript / Python. We recommend setting up a material loop where the Physical Material type is identified and then translated using Simplygon Shading Nodes. Keep in mind that "empty" texture nodes are not allowed, make sure that a valid texture is and that the checkbox is enabled, otherwise it is recommended to ignore creating the node or replace it with a color node.
Here's a snippet that will loop through available scene materials and list all material properties.
Which should give the following output:
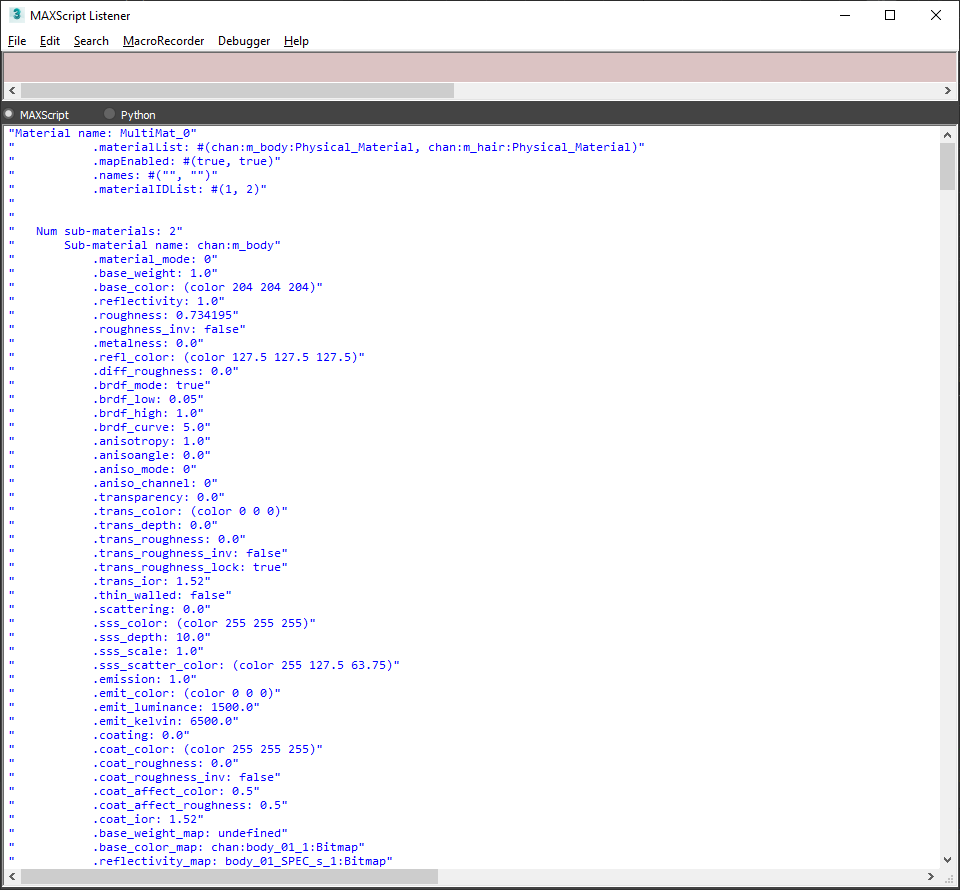
This is a short tutorial on how to use shading networks to translate a Physical Material to Simplygon material.
# Import
The Simplygon Max plug-in stores some material information from the last run which can be accessed via script. We will start by asking the plug-in for the material name of a mesh, material channels followed by textures.
Simplygon's "Physical Material" implementation is based on a collection of material channels, if these material channels are identified at import then Simplygon will hook in the result automatically. If custom channels are used, then they have to be handled manually by querying the plug-in and create the target material(s) manually and map back the information that was fetched from sgsdk_GetMaterialsForMesh, sgsdk_GetChannelsForMaterial, sgsdk_GetTexturePathForChannel and sgsdk_GetMappingChannelForChannel. We've excluded the material creation part from this tutorial as there usually are many lines of code and special conditions that does not really contribute that much. See the Physical Material example for a more detailed example.
# Related
Get to know how to work with Shading Networks: